Critical Chloride Thresholds (Ccrit) Concrete Durability Modelling
Why Critical Chloride Thresholds (Ccrit) Matter in Concrete Durability Modelling
Introduction
In the pursuit of more durable and sustainable concrete structures, one key factor stands out: the critical chloride threshold (Ccrit)—the concentration of chlorides that causes depassivation of steel reinforcement, initiating corrosion.
In 2022, the international working party fib TG 8.9.3 was formed to better define and apply Ccrit distributions in durability modelling. The aim: improve service life prediction tools and overcome the limitations of traditional “deemed-to-satisfy” (DtS) provisions found in most national codes.
What Is Ccrit—and Why Does It Matter?
Ccrit refers to the chloride concentration at which reinforcement in concrete begins to corrode. But it’s not a fixed value. It can vary significantly based on:
- Type of steel (e.g. carbon, stainless, galvanised)
- Concrete composition and quality
- Environmental conditions
- Testing and measurement method
The fib TG 8.9.3 working party, led by Frank Papworth, is developing a more accurate way to model and apply this critical variable using probabilistic distributions.
Beyond Deemed-to-Satisfy Rules
Most design standards offer DtS provisions—conservative rules designed to ensure safety under worst-case scenarios. However, they often:
- Over-design structures, wasting materials and cost
- Underperform in aggressive chloride environments
- Fail to account for site-specific variables
Probabilistic modelling provides flexibility, enabling engineers to optimise designs with real-world variables.
Understanding the Variability in Ccrit
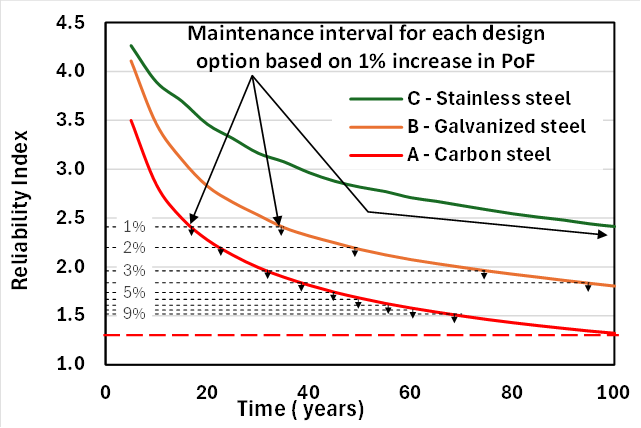
Ccrit measurement is highly variable. Different methods yield different results. Electrochemical tests detect early corrosion, while visual inspections detect it much later. Field variability adds to this complexity.
Ccrit Measurement Methods and Their Impact
BCRC’s Frank Papworth is the lead author of a recent technical paper from the fib TG 8.9.3 working group, which focuses on better defining the chloride concentration that depassivates reinforcement (Ccrit). This is a crucial parameter when modelling the service life of both new and existing reinforced concrete structures.
A key insight from the paper highlights how different methods used to measure Ccrit can yield significantly different values—a finding with major implications for durability design and life prediction models. The work aims to improve the consistency and reliability of Ccrit distributions for practical use in service life modelling.
An interesting aspect of the paper is the understanding of how different approaches to measuring Ccrit can yield significantly different values, as illustrated in the figure below.
Safeguarding Infrastructure: Deep Well ICCP System for Dubbo Bridge
Deep Well Impressed Current Cathodic Protection System for Steel Piles of a New Bridge Over a River
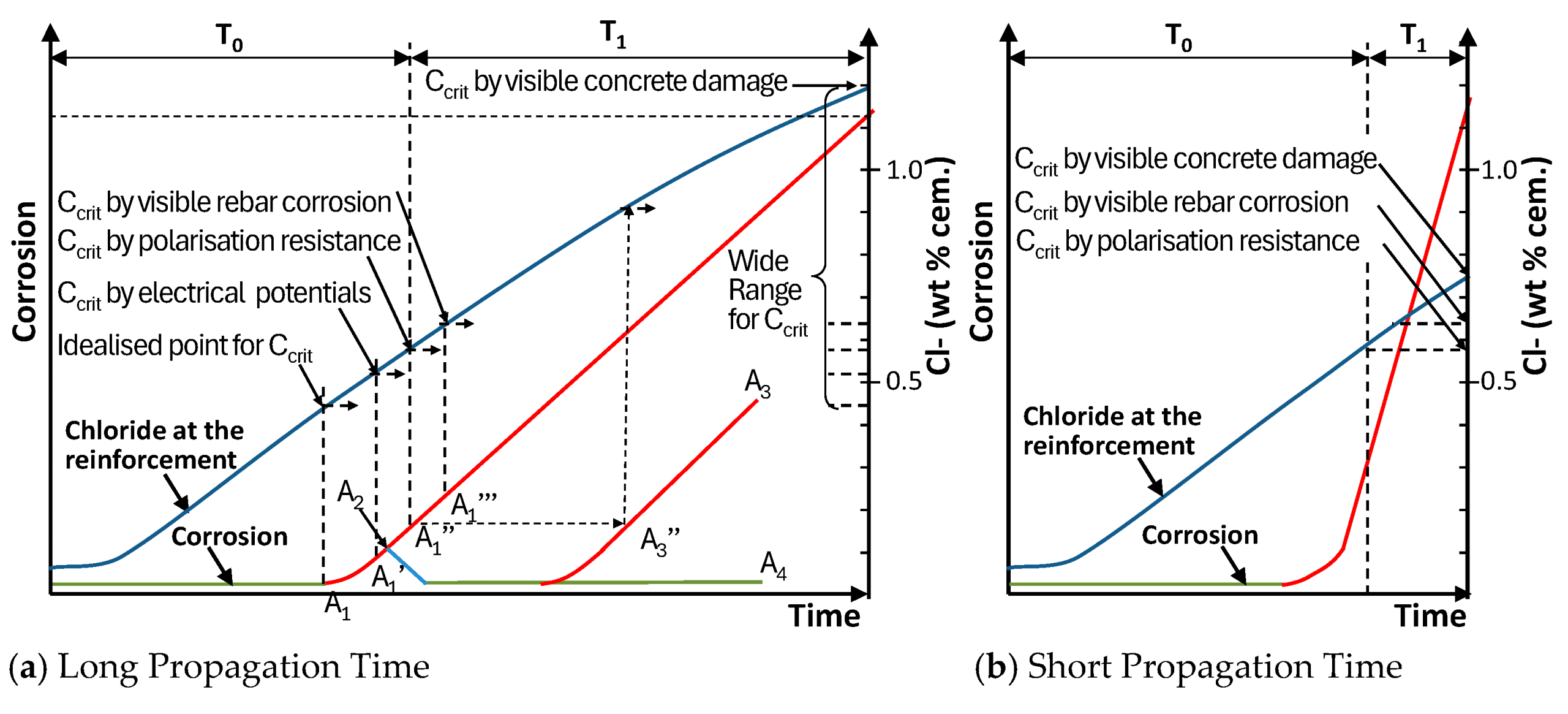
The New Dubbo Bridge project represents a major step forward in infrastructure development, aiming to enhance connectivity across the Macquarie River in New South Wales. This 662.59-meter-long bridge, supported by 19 piers extending up to 60 meters underground, relies on tubular steel piles as its foundation.
Safeguarding Infrastructure
Geotechnical surveys revealed a significant corrosion risk in the surrounding soil, leading to the innovative implementation of a Deep Well Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) system.
BCRC’s Innovative Approach
In a groundbreaking move, Saeed Ali, Senior Materials and Durability Engineer at BCRC, and Frank Papworth, Director at BCRC, collaborated to design a comprehensive ICCP system to protect the bridge’s steel piles from soil-induced corrosion.
Segmenting the bridge into seven zones, each zone was carefully analyzed based on soil resistivity and pile surface area ratios. SES CDEGS software played a key role in modelling ground-bed resistance and ground potential rise, ensuring a precise and effective design.
The project’s standout feature is the use of deep well anodes strategically placed under the bridge. This not only maximized efficiency but also minimized the need for additional installation space, thereby reducing project costs.
Environmental considerations were also addressed with cased and sealed anode systems, ensuring the sustainability of the design.
Safety and Sustainability at the Core
Step and touch voltage calculations were meticulously conducted to guarantee operational safety. By incorporating industry best practices and a focus on durability, this ICCP system sets a new benchmark in sustainable engineering. It highlights how innovative approaches can ensure critical infrastructure’s longevity and structural integrity.
A Case Study in Excellence
This project is a valuable case study demonstrating the effective application of cathodic protection techniques in large-scale infrastructure projects. It offers methodologies and insights that can be replicated globally, contributing to advancing sustainable engineering practices.
Top Image credit: Construction Review Online

View or download the full paper by Saeed Ali and Frank Papworth for a detailed look into this project’s design, implementation, and methodologies.
Effective Thermal Management in Precast Concrete
Effective Thermal Management in Precast Concrete for Major Infrastructure Projects
The Victoria Park-Canning Level Crossing Removal (LXR) Project is part of the Metronet infrastructure initiative. The project is Perth’s first major elevated rail designed to improve public transport safety, create new and versatile public spaces for the community, and reduce traffic congestion.
When complete, the Victoria Park-Canning Level Crossing Removal Project will feature five new, modern elevated stations, further enhancing connectivity and reducing travel disruptions across Perth. This milestone marks a significant step toward a more efficient and accessible public transport network for the city.
Thermal Management Challenges
BCRC tackled one of the biggest challenges in the precast concrete industry: managing heat during curing. With over 790 precast elements, including piers, Roofs, L-beams, and headstocks, manufactured for the project, implementing effective thermal management strategies was essential to maintaining structural integrity and meeting the tight schedule.
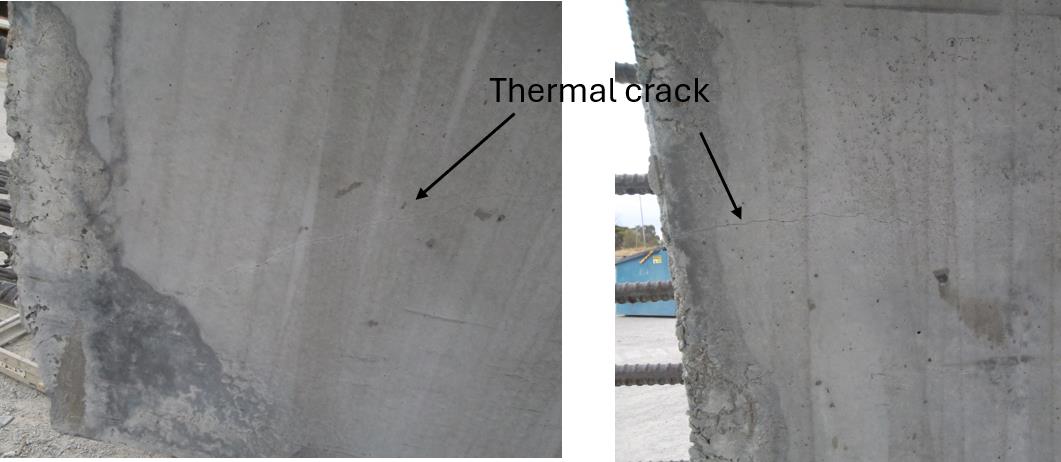
In precast concrete projects, heat of hydration, which is released during cement curing, can lead to thermal cracking and Delayed Ettringite Formation (DEF) if left unchecked. This project encountered added complexity due to the varied geometries and thicknesses of the elements, posing specific challenges:
1. High Binder Content Mixes:
These mixes were essential to achieve the rapid strength gains required but also significantly increased the internal heat, complicating temperature control.
2. Complex Geometries:
The varying thicknesses across different sections of the precast elements led to uneven heat distribution, making it difficult to ensure uniform cooling.
3. Accelerated Curing Requirements:
The project’s ambitious timeline necessitated fast curing, which amplified thermal control issues.
4. Maturity Considerations:
Different parts of each element cured at different rates, demanding close monitoring to avoid defects and inconsistencies.
Developing an Effective Thermal Control Plan
To overcome these challenges, the project team devised a comprehensive thermal control plan incorporating several key strategies:
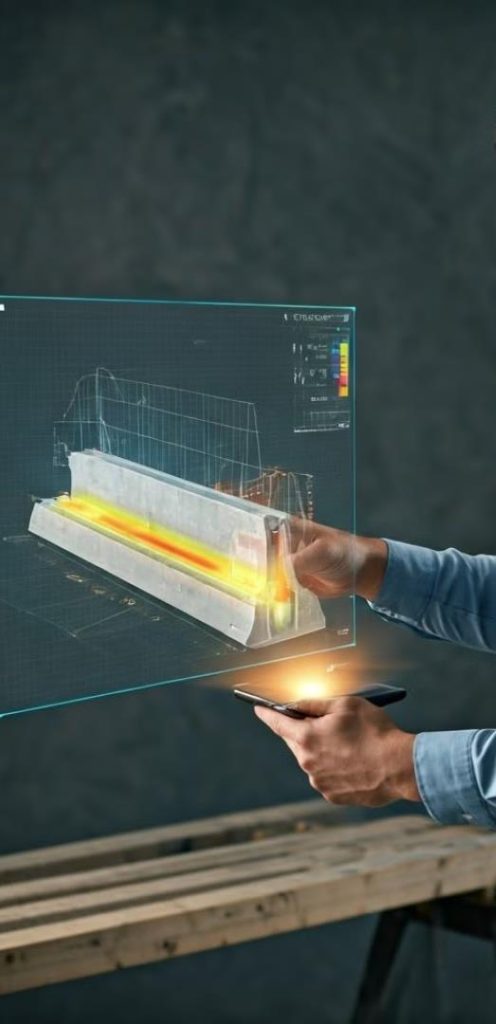
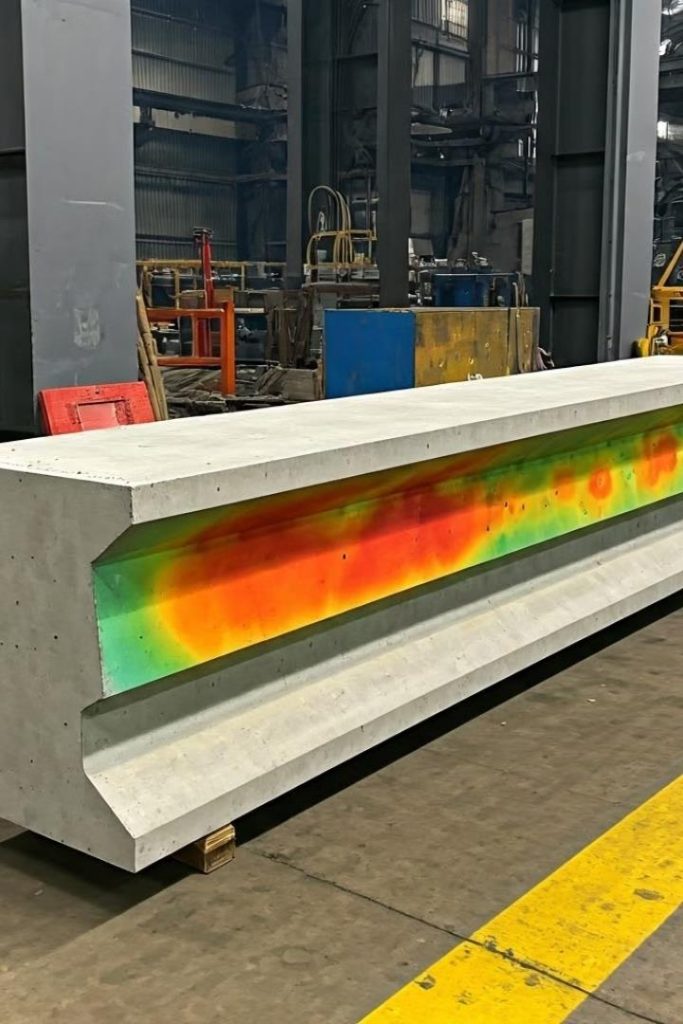
• FEM-Based Thermal Modelling:
This advanced modelling provided detailed insights into heat flow patterns, identifying hotspots and enabling targeted cooling interventions.
• Cooling Pipe System:
Embedded cooling pipes were strategically placed to dissipate heat in critical areas. Adjusting the pipes’ size, spacing, and flow rates allowed for consistent cooling across the elements.
• Optimized Steam Curing:
The team carefully adjusted the steam curing process to align with the natural heat of hydration, promoting uniform maturation.
• Real-Time Monitoring and Validation: Thermocouples embedded in the elements facilitated continuous temperature monitoring. This real-time data allowed for dynamic adjustments to the cooling system, ensuring effective thermal management.
Results and Key Takeaways
The thermal management strategies implemented on this project resulted in several notable outcomes:
• Minimal Cracking: Almost no significant thermal cracking was observed in the precast elements, demonstrating the effectiveness of the cooling and monitoring systems.
• Accelerated Construction: The ability to strip formwork in hours rather than weeks greatly streamlined the construction process.
• Specification Compliance: Temperature differentials were kept below the project’s stringent limits (70°C peak temperature and 20°C differential), confirming the project’s success in thermal management.


Key Takeaways for Future Projects
This case study offers important insights into the significance of effective thermal management in complex precast concrete projects:
1. FEM Modelling is Essential: Multi-dimensional thermal analysis allows for accurate predictions of peak temperatures and temperature gradients, particularly in complex structures.
2. Cooling Systems Are Crucial: A well-designed cooling system is indispensable for managing internal heat and preventing thermal cracking.
3. Continuous Temperature Monitoring: Real-time data enables immediate adjustments, ensuring consistent thermal control throughout the curing process.
4. Early Expert Engagement: Engaging thermal management experts early in the design phase can help pre-empt potential issues and streamline project execution.
This project underscores the critical role of robust thermal management in successfully executing large-scale infrastructure initiatives.
The Reliability Paradox – Marton Marosszeky
Life-Cycle Cost Analysis and Sustainability in Construction
Adopting sustainable practices for new structures is not just an environmental responsibility but a strategic approach to ensure their long-term viability and resilience. BCRC have made the point at many conferences that full probabilistic analysis (FPA) is currently the only approach to modelling durability as no other method calculates the likelihood of failure (i.e. corrosion initiation). While achieving a reliability of 1.3 at the end of the design life is deemed acceptable for most serviceability limit states it may not give the most economic cost over the deign life because it does not take into account the cost of minor repairs that are expected. If designed and constructed appropriately major repairs should not occur.
BCRC recently undertook a Life-Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) for a major jetty construction to compare the potential cost of different covers, mix designs and reinforcement types. In this case the construction costs were given by the contractor and the unit cost of a repair were assessed by BCRC based on accessibility. Operational and public costs can be the most significant part of a repair and hence these costs should be developed in conjunction with the client. On this project they were not major inputs. The client should also provide finance rates.
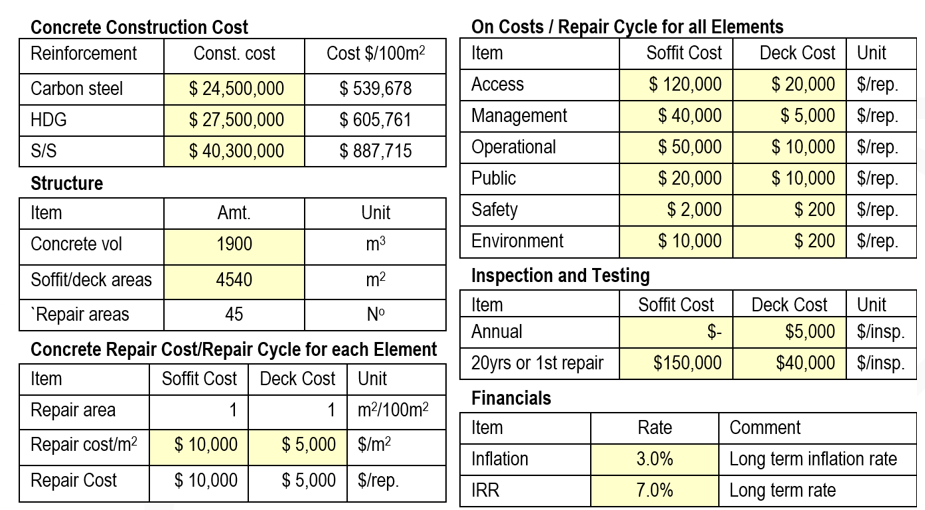
A critical aspect of the analysis is how frequently repairs will be required. In this case BCRC proposed assuming repairs would be undertaken when the probability of failure (PoF) for corrosion initiation increased by 1%. This was consistent with maintaining visual appearance more than structural concerns. As PoF is related to reliability the FPA provides the repair interval as shown in the reliability with time graph (standard FPA output) below. It compares the use of different reinforcement types for the same mix and cover. This was a small part of the much larger number of options considered.
The graph shows that stainless steel has such a high reliability that even at 100 years, no repairs were envisaged. The number of repair cycles increased to four for galvanised steel, and to around 12 for carbon steel. In this case repairs for carbon steel became so frequent that they were not tolerable, but by improving concrete performance and cover carbon steel was the lowest whole of life cost. On other projects where operational or public costs are high stainless steel may become the lowest cost.
Clearly FPA provides whether the reliability at the end of the design life is adequate but also, for any design approach, what the repair cycle and number of repairs for each cycle might be. BCRC’s Frank Papworth will be presenting this and other sustainability aspects for infrastructure at PIANC2024 in Sydney on 28 August.
BCRC as a Keynote Speaker Partner at Concrete 2021-Virtual Conference
- BCRC proudly announces its participation as a Keynote Speaker Partner for Oscar R. Antommattei at the CIA event – Concrete 2021 (5-8 September).
- Experience an engaging and exciting virtual program including keynote speakers, invited speakers and over 150 technical presentations. The four-day program will bring together global leaders in the concrete industry, covering all aspects of concrete materials, design, construction, repair, and maintenance, to discuss and share information on how innovation and smarter thinking will allow us to deal with disruption.
Don’t miss out and Register now!!!

Team BCRC is presenting Multiple Papers at CONCRETE 2021 (5-8th September):
Our director Frank Papworth will give a presentation on the importance of using the right model for durability design. He uses the simple graphs below to show that the equations used to predict depths of critical chloride level, and carbonation depth, over time must recognize that the variables in the formula are distributions. Because this is not fully detailed in simple models like Life 365 and CSTR 61 engineers judgement on the suitability of different materials is often flawed. The paper also explores they way forward with full probability analysis (FPA) in the design of structures.
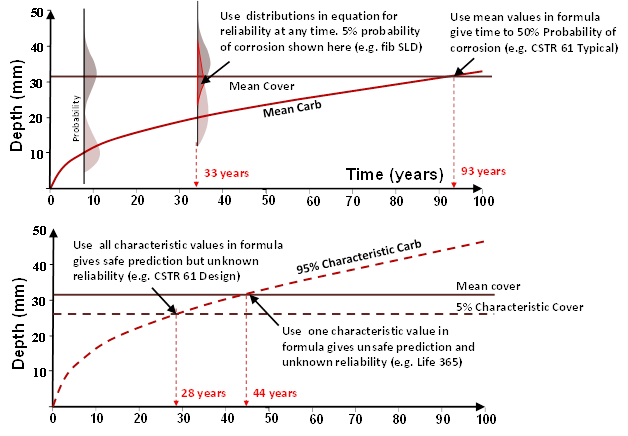
In a separate paper our Herman Jong shows how the FPA has been used to check AS5100.5 Deemed to Satisfy requirements. Frank will also team with Rodney Paul in a session on the work of the fib and CIA Durability Committees.
Quite separate to that our Gulraiz Ijaz presents on innovate sacrificial anode for cathodic protection that meet code criteria while our Robert Munn (Bob) provides an update on a lithium byproduct for use in concrete.
ACA Seminar ‘Maximising Durability in the Water Industry’
Mr Frank Papworth presented some thoughts on durability design based on BCRC’s experience on some major projects.
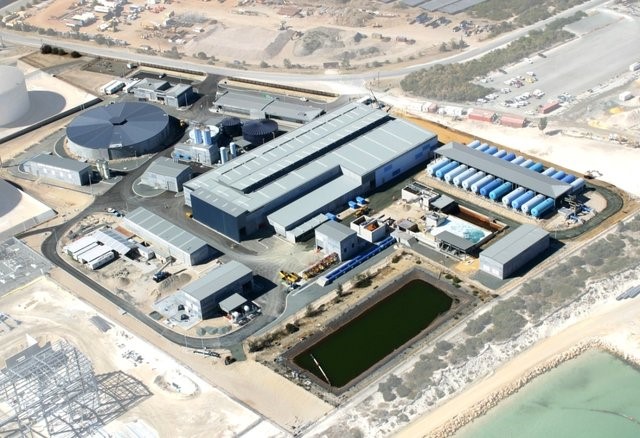
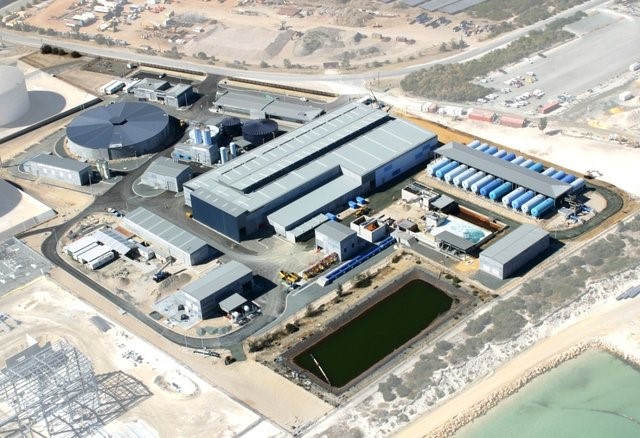
The first major desalination project in Australia (Perth Desalination Plant – right) showed the difficulty of correct exposure identification in process buildings. This has been a major failing on many building projects.
Other problems resolved on desalination projects included appropriate corrosion allowance for steel fibre segments for brine pitfalls, provisions for cathodic protection of diaphragm walls in severe exposures, exposure assessment of seawater tanks not kept full and crack control of tanks to prevent long term leakage.
The theme of crack control design was continued for large slab pours of Kalgoorlie’s 400GL reservoir (right), and particularly for settlements of inclined walls. The development of 100% joint testing by vacuum box was also described.
Experience with acid attack from hydrogen sulphide exposure centred on how limited attack of the concrete and reinforcement was ahead of the attacking front. The presentation concluded by showing the potential durability of concrete for water industry by discussing the inspections of three 100+ year old water tanks.